
Historically, alpha-theta training, a form of neurofeedback, was created to assist creativity by inducing hypnagogia, a "borderline waking state associated with creative insights", through facilitation of neural connectivity. A study with conservatoire musicians found that alpha-theta training benefitted the three music domains of musicality, communication, and technique. The applications of neurofeedback to enhance performance extend to the arts in fields such as music, dance, and acting. The most common protocol for seizure control was sensorimotor rhythm (SMR), which was found to significantly reduce weekly seizures. Neurofeedback has been found to be a viable alternative for patients who did not find benefit from other medical treatment.
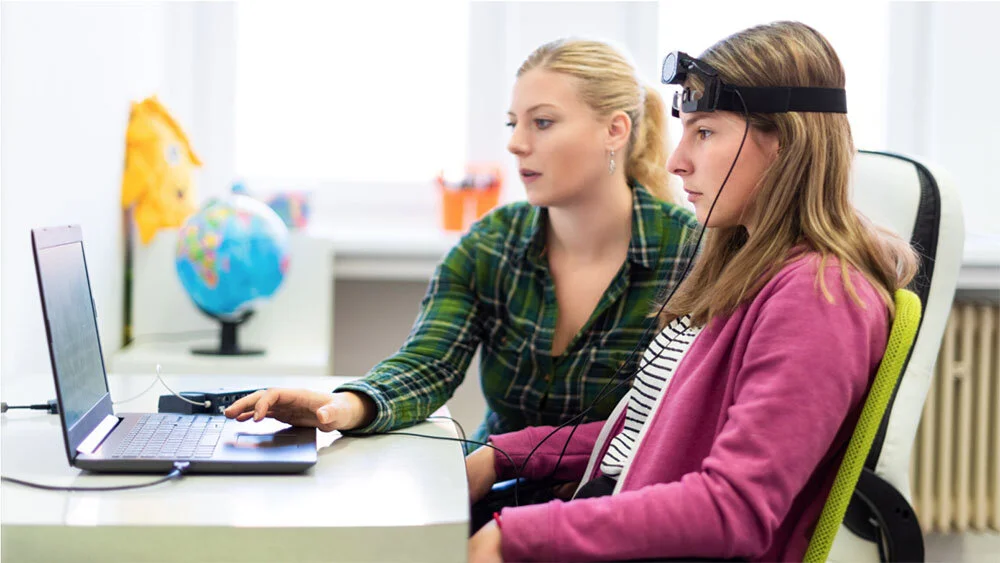

Neurofeedback has been also found to be generally positive for stroke recovery, with improvements found in motor function and behavior comparable with conventional occupational therapy. Neurofeedback has been used to treat traumatic brain injury (TBI) in military and civilian populations. Individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) also have been found to benefit from neurofeedback, including children with developmental trauma. Neurofeedback training, particularly localized neurofeedback training, has been found to be therapeutic for patients for depression and self-regulation. Standard neurofeedback protocols for ADHD include theta/beta, SMR and slow cortical potentials are well investigated and have demonstrated specificity. Recent investigation into the effectiveness of neurofeedback for ADHD has found neurofeedback to have durable effects following treatment, although prior work has contradicted this conclusion. Since the first reports of neurofeedback treatment in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in 1976, many studies have investigated the effects of neurofeedback on different symptoms of ADHD such as inattention, impulsivity and hyperactivity. Related technologies include functional near-infrared spectroscopy-mediated (fNIRS) neurofeedback, hemoencephalography biofeedback (HEG) and fMRI biofeedback. Several neurofeedback protocols exist, with additional benefit from use of quantitative electroencephalography (QEEG) or functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to localize and personalize treatment. NFB is relatively non-invasive and is administered as a long-term treatment option, typically taking a month to complete. There is significant evidence supporting neurotherapy for generalized treatment of mental disorders, and it has been practiced over four decades, although never gaining prominence in the medical mainstream. Typically, electrical activity from the brain is collected via sensors placed on the scalp using electroencephalography (EEG), with feedback presented using video displays or sound. Neurofeedback ( NFB), also called neurotherapy, is a type of biofeedback that presents real-time feedback from brain activity in order to reinforce healthy brain function through operant conditioning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
